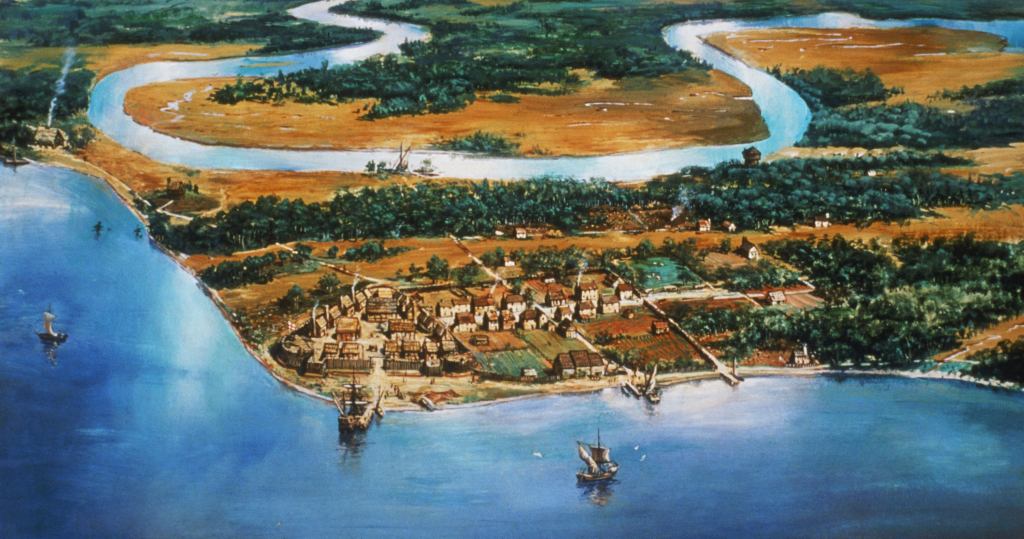
The Jamestown colony was founded in 1607 by the Virginia Company, a joint-stock company that received a royal charter from King James I. Unlike previous failed colonies like Roanoke, Jamestown, against great odds, would go on to become the first permanent English colony in North America. From Jamestown, settlers would branch out beyond the early colony site. The Jamestown site was located on a peninsula (now an island) in the James River, about 60 miles from the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay. Jamestown faced many challenges and hardships in its early years, such as famine, disease, conflict with Native Americans, and internal strife. Jamestown would survive and become the site of many important events and developments in American history, such as the first representative assembly, the first arrival of African slaves in 1619, and the cultivation of tobacco.
The Founding of Jamestown
The Virginia Company was formed in 1606 with the aim of establishing a profitable colony in North America. The company sent three ships, the Susan Constant, the Godspeed, and the Discovery, with 104 men and boys, to explore the coast of Virginia and find a suitable location for a settlement. The expedition was led by Captain Christopher Newport, who had the sealed instructions from the company that contained the names of seven members of the governing council. Among the colonists were gentlemen, craftsmen, laborers, and adventurers, as well as Captain John Smith, a former soldier and explorer who had been accused of mutiny during the voyage.
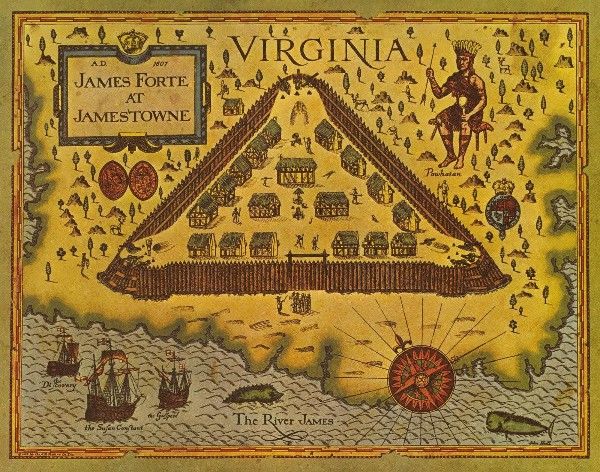
The ships arrived at the Chesapeake Bay in April 1607 and sailed up the James River, named after the king. They chose a site for the settlement on May 13, 1607, and named it Jamestown. The site was a peninsula, which made it easy to defend from possible Spanish attacks, and had deep water ports for anchoring ships. However, the site also had many disadvantages, such as being marshy, mosquito-infested, and prone to droughts and floods. The site was also within the territory of the Powhatan Confederacy, a powerful alliance of about 30 Algonquian-speaking tribes led by Chief Powhatan, who controlled most of the coastal Virginia region.
The colonists quickly built a triangular fort with a storehouse, a church, and several houses. They also planted crops and traded with the Native Americans for food and supplies. However, they soon faced many difficulties because most of the men were set on finding gold, and they did not grow enough crops. This led to hard times exacerbated by food shortages, diseases, poor leadership, and conflicts with the Powhatan. John Smith held the colony together by forcing the colonists to farm. Many of the colonists died in the first year, and the survivors were demoralized and desperate. In June 1607, Newport returned to England with two ships and 40 men, leaving behind 104 colonists. He brought back a load of sassafras, a plant that was believed to have medicinal properties, and a letter from Smith that exaggerated the prospects of the colony. Newport also promised to return with more supplies and settlers within six months.

The Starving Time and the Arrival of Lord De La Warr
John Smith was an adventurer who had fought in wars and had been captured by pirates. Later in life, he claimed to have been saved by Pocahantas, the daughter of Chief Powhatan, after being captured by the chief in December 1607. Smith claimed that Pocahantas had intervened to prevent him from being executed by her people, and that she had created peace between the English settlers and the Natives. Many historians today doubt the accuracy of his stories, and suggest that he either misunderstood the incident or embellished it for fame or notoriety.
As leader of the Jamestown colony in its early days, Smith imposed strict discipline and brought order to the colony. He explored the Chesapeake Bay and Potomac River, and created maps and reports of the region. He forced the colonists to build houses, clear land, plant crops and hunt for food. He traded with the natives and established friendly relations with the tribes.
Smith’s leadership helped the colony survive for about two years. In October 1609, a stray spark ignited a gunpowder bag John Smith was wearing, while he was in a canoe. Badly burned, Smith headed back to England for treatment, leaving Jamestown to fend for itself. His departure marked the beginning of the worst period in the history of Jamestown, known as the “Starving Time” in which only 60 of the 600 new colonists survived. The “Starving Time” lasted during the winter of 1609-1610 when the colony was besieged by the Powhatan, who cut off their food supply and killed anyone who ventured out of the fort. The colonists resorted to eating roots, rats, snakes, boiled shoe leather, horses, dogs, cats, and even human corpses.
The colony was on the verge of collapse, when a fleet of three ships arrived in June 1610, bringing 150 new settlers and supplies, as well as a new governor, Lord Thomas West, known as Lord De La Warr. He was a veteran soldier and a nobleman, who had been appointed by the Virginia Company as the first permanent governor of Virginia. He brought with him a new charter, which granted more powers and privileges to the company, and a new policy of aggressive expansion and warfare against the Powhatan. De La Warr also arrived just in time to stop the remaining colonists from abandoning Jamestown and returning to England on the ships that had brought them. He ordered them to turn back and rebuild the colony, and vowed to make Jamestown a success.

The Tobacco Boom
One of the most significant developments in the history of Jamestown was the introduction and cultivation of tobacco, which became the main export and source of wealth for the colony. Tobacco was a native plant of the Americas, and was used by the Native Americans for ceremonial and medicinal purposes. The Europeans became addicted to tobacco after encountering it in the Caribbean and South America, and the demand for tobacco in Europe grew rapidly in the 17th century. The Virginia Company saw tobacco as a potential cash crop that could make the colony profitable and attract more settlers and investors.
The first person to successfully grow tobacco in Virginia was John Rolfe, a colonist who had arrived in Jamestown in 1610. Rolfe experimented by cross breeding tobacco from Bermuda with a strain that local Native Americans had grown for years. He also developed a curing process that improved the quality and flavor of the tobacco. Rolfe’s tobacco was well received in England, and he shipped the first commercial cargo of tobacco from Virginia in 1614. He also married Pocahontas, the daughter of Powhatan, in 1614, which created a temporary peace between the English and the Powhatan.
The success of Rolfe’s tobacco sparked a tobacco boom in Virginia. Soon, tobacco was referred to as “Brown Gold.” Tobacco became the main currency and cash crop of Virginia, and attracted more settlers and investors. The tobacco boom also saw the increase in labor by indentured servants, and later, slaves.

The Legacy of Jamestown
Jamestown laid down the foundations of long lasting institutions in English America. A great paradox took place in the colony in 1619, which would change the course of history in North America. The year 1619 witnessed the first representative government in English North America, as well as the first Africans arriving in English North America, a dichotomy of both freedom and bondage.
The House of Burgesses allowed voters to elect representatives to create laws in the colony. This groundbreaking experiment was the first representative assembly in North America, in which free, male, property-owners elected representatives. However, in the same year, Africans first arrived in Virginia aboard a Dutch merchant ship called the White Lion. At first, Jamestown colonists treated them as indentured servants, much in the same way as white indentured servants from England. After a few years, most Africans received land and freedom. However, over time, a racial caste was formed in which Africans became permanent slaves, a trend believed to have been developed by the 1640s. Jamestown witnessed freedom in a representative body on one hand, and slavery and bondage on another. The concept of freedom for some and bondage for others would be a primary and complicated debate within North America for centuries to come.
Jamestown remained the capital of Virginia until 1699, when it was moved to Williamsburg. By then, Jamestown had expanded from its original fort to a town with several public buildings, such as a statehouse, a church and a courthouse.
Jamestown was gradually abandoned after its statehouse burned down in 1698. It became a ghost town until it was rediscovered in the late 19th century. In 1934, it was declared a National Historic Site by Congress. Today, it is part of the Colonial National Historical Park, which also includes Yorktown and Williamsburg. Visitors can see the remains of the original fort, as well as reconstructed buildings and exhibits that showcase the life and history of Jamestown.
Sources:
Encyclopædia Britannica, inc. (2023, October 25). Jamestown colony. Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/Jamestown-Colony
A&E Television Networks. (n.d.). Jamestown colony – facts, founding, Pocahontas. History.com. https://www.history.com/topics/colonial-america/jamestown
Jarus, O. (2022, May 31). Jamestown Colony: Facts & History. LiveScience. https://www.livescience.com/38595-jamestown-history.html
World History Edu. (2020, September 15). Jamestown Colony: England’s first, thriving settlement in the Americas. https://www.worldhistoryedu.com/jamestown-history-significance-facts/
Historicjamestowne.org
Yost, R. (2023, November 11). Jamestown colony facts and story. The History Junkie. https://thehistoryjunkie.com/jamestown-colony-facts/