In (Part 1) and (Part 2) of my blog post on the Lincoln Assassination, I discussed the assassin, John Wilkes Booth, and the events that unfolded on the evening of April 14, 1865. Part 3 will focus on the death of Lincoln and the widspread manhunt for Booth. I also ponder the question: What if Lincoln had lived?
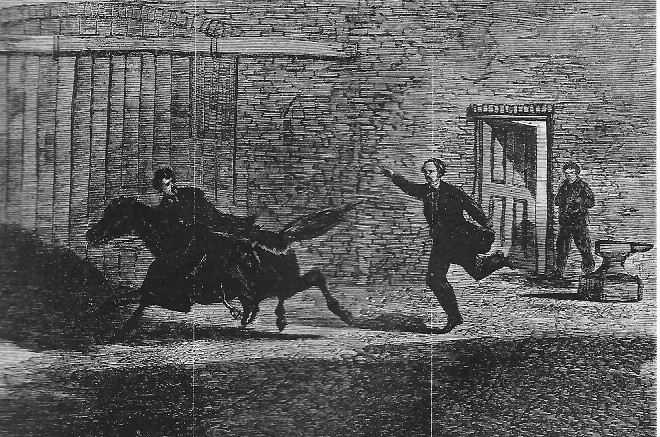
After Booth shot Lincoln at 10:15pm at the Ford’s Theatre, he escaped out of a side door and mounted a horse for his getaway. At about 11:30pm, Booth met up with co-conspirator David Herold and headed south. They arrived at the home of Dr. Samuel Mudd whom examined Booth’s broken ankle. Once Mudd realized that Booth was a fugitive on the run, Mudd asked the conspirators to leave.
They then moved on as fugitives in hiding, making a couple of stops at the homes of Confederate sympathizers. (American Experience, PBS) Booth was able to get his hands on local newspapers. While he thought the country, especially the south, would be praising him, he found that the country was condemning him. Throughout his escape, Booth kept a journal and in it he wrote, “I struck boldly and not as the papers say… our country owed all our troubles to him and God simply made me, the instrument of his punishment.” (American Experience, PBS) Booth believed that the country would be singing his praise for his bold action. However, Booth discovered that not to be true.
At 7:22 A.M. on April 15th, 1865, Abraham Lincoln died. Lincoln became the first president who was ever assassinated. After the war ended on April 9th, the Union had reason to celebrate. The bloody, four year struggle between the North and the South was finally over. Lincoln had succeeded in preserving the Union and issuing the Emancipation Proclamation. But now just a few days later, the country was mourning its fallen hero. The New York Herald said, “The sun set last night on a jubilant and rejoicing nation. It rose this morning upon sorrow stricken people.” (American Experience, PBS) The day after Lincoln died was Easter Sunday. Preachers around the country devoted their sermons to the memory of Lincoln. He was now seen as a martyr who died to unify the country. (American Experience, PBS) Besides mourning and grief, there was also anger in the North. Mobs formed in cities around the country showing rage and violence towards anyone who identified with the Confederacy or the Democratic Party. Most Southerners publicly expressed condolences, but privately did view Booth as the American Brutus that Booth believed he was. (American Experience, PBS)

By April 20th, 1865, most of the conspirators had been caught, but Booth and Harold were still on the run. The hunt for Booth became the largest manhunt in American history, with a reward of $100,000 for his capture. (American Experience, PBS) During the manhunt, Booth wrote that he’d been hunted like a dog through swamps and woods, “for doing what Brutus was honored for, and yet I, for striking down a greater tyrant than he ever knew, was looked upon as a common cutthroat.” (American Experience, PBS) In his writing, we again see that Booth considered himself a hero, and yet, the public only viewed him as the murderer of a great man.

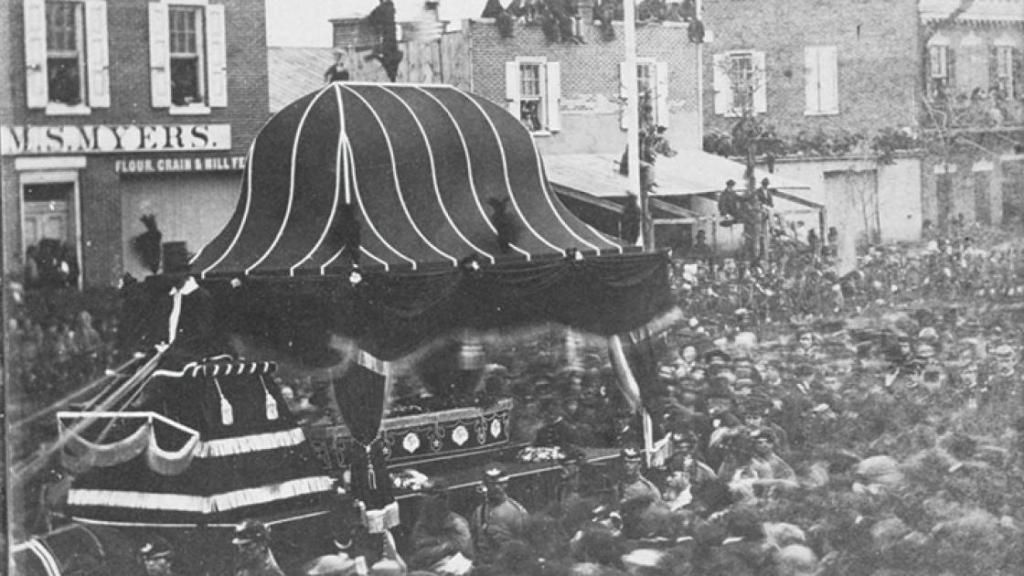
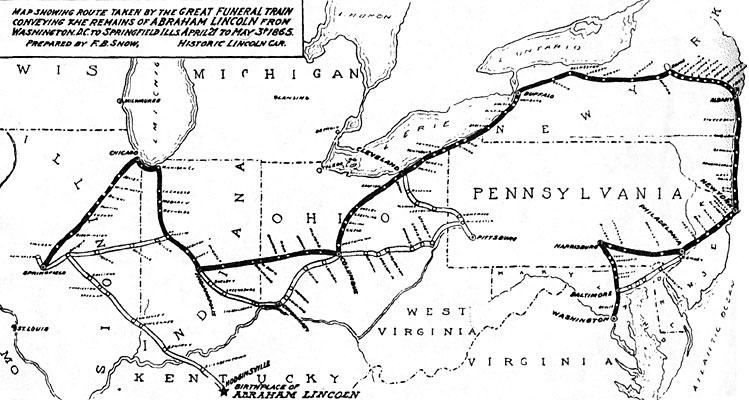
On April 21st, 1865, Lincoln’s funeral train, draped in black, departed from Washington. For 12 days, the train travelled over 1,600 miles to major cities around the country. Approximately 7 million Americans, almost a third of the Union’s population turned out to mourn their hero’s death. (McDougal, p. 371) As they mourned the death of Lincoln, they were also mourning for the lives of the hundreds of thousands lost in the war. The funeral train made its final stop in Lincoln’s hometown of Springfield, IL where he would be buried. (American Experience, PBS) Lincoln had become a larger than life folk hero after his assassination. People respected and honored him for the way he courageously carried the country through the most trying times. The weight of the country was on his shoulders and he ultimately became a martyr for the cause of union, democracy and freedom.

On April 26th, Union cavalry closed in on Booth and Herold at the Garret Farm in Virginia. The cavalry surrounded a barn where the two men hid. Herold surrendered but Booth refused. The cavalry set the barn of fire. As Booth tried to escape, he was shot by Sergeant Boston Corbett and died on April 26th, 1865. (American Experience, PBS) Booth is said to have whispered, “Tell my mother I died for my country. I did what I thought was best.” (McDougal, p. 370) Booth’s other conspirators were either sentenced to death or life in prison.

The manhunt was over. While the country was relieved that Booth was caught, they still mourned for the life of Abraham Lincoln. The country was never given an opportunity to see how Lincoln would have carried out the Reconstruction of the country. That task would fall into the hands of his successor, Andrew Johnson. Lincoln’s legacy and impact on the United States will always be in the minds and hearts of the American people. He preserved the Union and fought for the passage of the 13th Amendment which emancipated the roughly 4 million slaves in the country. When Lincoln died on April 15th, Secretary of War Edwin Stanton was by his side and stated the famous line. “Now he belongs to the ages.” (American Experience, PBS)
What If?
Sometimes I wonder, what if Lincoln lived to serve out his second term? How would history have played out differently? We know that the Reconstruction Era under his successor, Andrew Johnson, went terribly to say the least. Johnson was impeached and was constantly at odds with the Radical Republicans in Congress. Would Lincoln have gotten along with and agreed with the Radical Republicans in Congress about how to handle Reconstruction? Lincoln was more moderate than many of them with his Ten Percent Plan for allowing the former Confederate states back into the country. Would many of the Radical Republicans bend to some of Lincoln’s views? How would Lincoln have helped freed African Americans after the war? We know that Johnson did virtually nothing to help them. It’s likely that they would have gained more opportunities under the Lincoln administration. How would Lincoln have handled post-war challenges? We can only speculate that a character like Lincoln would have done a much more effective job of carrying the country through the challenges of Reconstruction. How would Lincoln have been remembered had he lived? We know in reality that he was viewed as a martyr who saved the Union and has always been ranked either the best or in the top 2 presidents of all time. He definetely would have been revered for what he accomplished but he wouldn’t have been elevated to the status of a martyr. Assuming he had an effective second term, we can assume he would still be ranked amongst the best presidents, but what if his second term didn’t go well? Where would he be ranked then? These questions can’t be answered with certainty but it’s always interesting to the ask the, “What If”? Any thoughts on the matter, please comment below.

Related Posts:


